This time I decided to do a blog post about the HPE Smart Array RAID controllers with their wonderful ssacli tool. The tooling of HPE is very powerful because you can online manage a VMware ESXi host and migrate for example from a RAID 1 volume to a RAID 10 without downtime or change the read and write cache ratio.
So far as I know I haven’t seen an identical tool yet from the other server hardware vendors like Cisco, Dell EMC, IBM, and Supermicro. The main difference has always been that the HPE tool can perform the operation live without downtime.
So far as I can remember it has been there for ages. It was already available for VMware ESX 4.0 and is still available in VMware ESXi 6.7. So thumbs-up for HPE :).
Let’s talk about controller support. The tool supports the most HPE SmartArray controllers over the last 10 to 15 years, for example, the Smart Array P400 was released in 2005 and is still working fine today.
Here is an overview of supported controllers:
- HPE Smart Array P2XX
- HPE Smart Array P4XX
- HPE Smart Array P7XX
- HPE Smart Array P8XX
HPE SSACLI – Location
In case you are using the HPE VMware ESXi custom images. The tool is already pre-installed when installing ESXi. The tool is installed as a VIB (vSphere Installable Bundle). This means it can also be updated with vSphere Update Manager.
Over the years the name of the HPE Storage Controller Tool has been changed and so has the location. Here is a list of locations that have been used for the last ten years for VMware ESXi:
# Location VMware ESXi 4.0/4.1/5.0
/opt/hp/hpacucli/bin/hpacucli
# Location VMware ESXi 5.1/5.5/6.0
/opt/hp/hpssacli/bin/hpssacli
# Location VMware ESXi 6.5/6.7
/opt/smartstorageadmin/ssacli/bin/ssacliHPE SSACLI – Examples
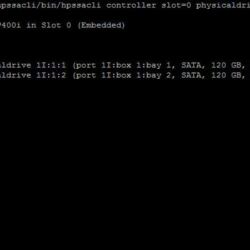
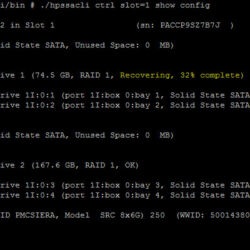
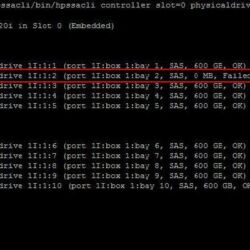
I have collected some screenshots over the years. Screenshots were taken by doing maintenance on VMware ESXi servers. The give you an idea what valuable information can be shown.
HPE SSACLI – Abréviation
All commands have a short name to reduce the length of the total input provided to the ssacli tool:
### Shortnames:
- chassisname = ch
- controller = ctrl
- logicaldrive = ld
- physicaldrive = pd
- drivewritecache = dwc
- licensekey = lk
### Specify drives:
- A range of drives (one to three): 1E:1:1-1E:1:3
- Drives that are unassigned: allunassignedHPE SSACLI – Status
To view the status of the controller, disks or volumes you can run all sorts of commands to get information about what is going on in your VMware ESXi server. The extensive detail is very useful for troubleshooting and gathering information about the system.
# Show - Controller Slot 1 Controller configuration basic
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 show config
# Show - Controller Slot 1 Controller configuration detailed
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 show detail
# Show - Controller Slot 1 full configuration
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 show config detail
# Show - Controller Slot 1 Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 show status
# Show - All Controllers Configuration
./ssacli ctrl all show config
# Show - Controller slot 1 logical drive 1 status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 1 show status
# Show - Physical Disks status basic
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd all show status
# Show - Physical Disk status detailed
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd all show status
# Show - Logical Disk status basic
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld all show status
# Show - Logical Disk status detailed
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld all show detailHPE SSACLI – Creating
Creating a new logical drive can be done online with the HPE Smart Array controllers. I have displayed some basic examples.
# Create - New single disk volume
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 create type=ld drives=2I:0:8 raid=0 forced
# Create - New spare disk (two defined)
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 array all add spares=2I:1:6,2I:1:7
# Create - New RAID 1 volume
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 create type=ld drives=1I:0:1,1I:0:2 raid=1 forced
# Create - New RAID 5 volume
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 create type=ld drives=1I:0:1,1I:0:2,1I:0:3 raid=5 forcedHPE SSACLI – Adding drives to logical drive
Adding drives to an already created logical drive is possible with the following commands. You need to perform two actions: adding the drive(s) and expanding the logical drive. Keep in mind: make a backup before performing the procedure.
# Add - All unassigned drives to logical drive 1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 1 add drives=allunassigned
# Modify - Extend logical drive 2 size to maximum (must be run with the "forced" flag)
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 2 modify size=max forcedHPE SSACLI – Rescan controller
To issue a controller rescan, you can run the following command. This can be interesting for when you add new drives in
### Rescan all controllers
./ssacli rescanHPE SSACLI – Drive Led Status
The LED status of the drives can also be controlled by the ssacli utility. An example is displayed below how to enable and disable a LED.
# Led - Activate LEDs on logical drive 2 disks
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 2 modify led=on
# Led - Deactivate LEDs on logical drive 2 disks
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 2 modify led=off
# Led - Activate LED on physical drive
./ssacli ctrl slot=0 pd 1I:0:1 modify led=on
# Led - Deactivate LED on physical drive
./ssacli ctrl slot=0 pd 1I:0:1 modify led=off
HPE SSACLI – Modify Cache Ratio
Modify the cache ratio on a running system can be interesting for troubleshooting and performance beanchmarking.
# Show - Cache Ratio Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify cacheratio=?
# Modify - Cache Ratio read: 25% / write: 75%
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify cacheratio=25/75
# Modify - Cache Ratio read: 50% / write: 50%
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify cacheratio=50/50
# Modify - Cache Ratio read: 0% / Write: 100%
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify cacheratio=0/100HPE SSACLI – Modify Write Cache
Changing the write cache settings on the storage controller can be done with the following commands:
# Show - Write Cache Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=?
# Modify - Enable Write Cache on controller
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=enable forced
# Modify - Disable Write Cache on controller
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=disable forced
# Show - Write Cache Logicaldrive Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 logicaldrive 1 modify aa=?
# Modify - Enable Write Cache on Logicaldrive 1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 logicaldrive 1 modify aa=enable
# Modify - Disable Write Cache on Logicaldrive 1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 logicaldrive 1 modify aa=disableHPE SSACLI – Modify Rebuild Priority
Viewing or changing the rebuild priority can be done on the fly. Even when the rebuild is already active. Used it myself a couple of times to lower the impact on production.
# Show - Rebuild Priority Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify rp=?
# Modify - Set rebuildpriority to Low
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify rebuildpriority=low
# Modify - Set rebuildpriority to Medium
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify rebuildpriority=medium
# Modify - Set rebuildpriority to High
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify rebuildpriority=highHPE SSACLI – Modify SSD Smart Path
You can modify the HPE SDD Smart Path feature by disabling or enabling. To make clear what the HPE SDD Smart Path includes, here is
“HP SmartCache feature is a controller-based read and write caching solution that caches the most frequently accessed data (“hot” data) onto lower latency SSDs to dynamically accelerate application workloads. This can be implemented on direct-attached storage and SAN storage.”
For example, when running VMware vSAN SSD Smart Path must be disabled for better performance. In some cases worse the entire vSAN disk group fails.
# Note: This command requires the array naming type like A/B/C/D/E
# Modify - Enable SSD Smart Path
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 array a modify ssdsmartpath=enable
# Modify - Disable SSD Smart Path
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 array a modify ssdsmartpath=disableHPE SSACLI – Delete Logical Drive
Deleting a logical drive on the HPE Smart Array controller can be done with the following commands.
# Delete - Logical Drive 1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 1 delete
# Delete - Logical Drive 2
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 2 deleteHPE SSACLI – Erasing Physical Drives
In some cases, you need to erase a physical drive. This can be performed with multiple erasing options. Also, you can stop the process.
Erase patterns available:
- Default
- Zero
- Random_zero
- Random_random_zero
# Erase physical drive with default erasepattern
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 2I:1:1 modify erase
# Erase physical drive with zero erasepattern
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 2I:1:1 modify erase erasepattern=zero
# Erase physical drive with random zero erasepattern
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 1E:1:1-1E:1:3 modify erase erasepattern=random_zero
# Erase physical drive with random random zero erasepattern
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 1E:1:1-1E:1:3 modify erase erasepattern=random_random_zero
# Stop the erasing process on phsyical drive 1E:1:1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 1E:1:1 modify stoperaseHPE SSACLI – License key
In some cases a licence key needs to be installed on the SmartArray storage controller to enable the advanced features. This can be done with the following command:
# License key installation
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 licensekey XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX
# License key removal
./ssacli ctrl slot=5 lk XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX delete Related sources
A couple of interesting links related to the HPE Storage Controller tool for VMware ESXi:


Useful article, thank you very much!
you can do this DELL server by installing a small utility that lives on the EXSi host. It works on a single host (so no need for vCENTER)
you can change the raid, re-build it, expand it, etc, etc,
This is the CLI version
https://www.virtualizationhowto.com/2017/11/manage-dell-raid-in-vmware-esxi-6-5-with-perccli/
There is also a GUI version which I have used before.
Hello Ian,
Thanks for reaching out and sharing the information!
It is too bad it is not included out of the box. The hpssacli/ssacli does also not require a vCenter Server.
Best regards,
Mischa Buijs
Can I use this utility offline?
What do you mean with offline?
Thanks for the commands, How about migration from RAID 1 to RAID 5?
Depending on the controller and license it could be possible. I have not tested this yet!
I think the command to install the license key is not correct, the correct command is:
ssacli ctrl slot=1 add licensekey=XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX
The command provided in the article just selects all controllers with the specified license key already installed, it does not add any license key.
Thanks for responding and improving this blog post. I think you are right :).
One note on these commands
Show – Write Cache Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=?
# Modify – Enable Write Cache on controller
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=enable forced
# Modify – Disable Write Cache on controller
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=disable forced
These are to enable/disable drive write cache on the SSD itself NOT the controller. These should be used with caution. If you are not using Enterprise class SSD with cache backup technology on the drives then setting these options could cause data loss. If you are using consumer grade drives such as in a lab environment I would probably leave drive write cache disabled.
from the manual
Enabling or disabling the drive cache
On controllers and drives that support physical drive write cache, you can use this command to enable or disable the write cache for all drives on the controller.
CAUTION: Because physical drive write cache is not battery-backed, you could lose data if a power failure occurs during a write process.
To minimize this possibility, use a backup power supply.
Syntax: modify drivewritecache=enable|disable|? [forced]
Your article was extremely useful. Gud work! Much valued, continue posting some more.
Absolute god send of a page. Thanks!
Ion casino is a trusted and best online casino site through 2010 which includes dished up
millions of participants in Asia. Ion casino or also known as Ionclub is typically the
top ranking option site because this provides the best experience for gambling online players in Philippines.
With an recognized license to function, this provider ensures that players
create bets without danger, credibility and may be depended on.
Can anyone tell me how to enable a drive that has been set as a spare so that it’s space can be used? I’ve tried the add drives command but no go… 🙁
ctrl slot=0 array A remove spares=2I:1:8
Figured it out… Shared as example.
Useful article,thank you very much!
Thanks Aaron!
Nice Article.
Hello, if I run this command:
./ssacli ctrl all show config
The response is:
Smart Array P440ar (Error: Not responding)
Do you have any idea? Can you please help me?
Thank you
Hello Nela,
This could be related to a combination of firmware and software (they might be incompatible).
I have seen this error sometimes and was resolved by an update or a reboot.
Regards,
Mischa
Hello everyone,
Is it just me, or the most important command is missing? How do you start the rebuild of an array with a failed disk without rebooting the server? RAID5 or RAID1 for instance…
That happens automatically, just remove the dead disk and install the new disk. No command is required.
Ok, thank you.
I have an hp dl380 g9 which has couple spare drives in slot. controller=P840.
Can i just replace a dead drive in an RAID 5 array by: – removing an ‘unassigned’ drive from the same server and putting it in place of the dead drive?
Will it not confuse the controller about its drive ‘addressing’ ?
Thank you.
Make sure the drive you put in as a replacement is fully wiped. To make sure you don’t confuse the controller.
My ESXi has Array A and B and 3 unassigned drives. How can I create a new Array C with RAID5?
Unassigned
physicaldrive 1I:1:6 (port 1I:box 1:bay 6, SAS HDD, 1 TB, OK)
physicaldrive 1I:1:7 (port 1I:box 1:bay 7, SAS HDD, 1 TB, OK)
physicaldrive 1I:1:8 (port 1I:box 1:bay 8, SAS HDD, 1 TB, OK)
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 create type=ld drives=1I:1:6,1I:1:7,1I:1:8 raid=5 forced
correct?
Sounds correct to me!
I’m trying to determnine the size of my battery backed Cache module. So I’ve issued this command:
/opt/smartstorageadmin/ssacli/bin/ssacli ctrl all show detail | grep -i cache
This produces the nfollowing output. The cache sizes are denoted as 2.0 and 1.8. But this has no unit behind it. So what unit is implied here?
I assume GB?
I’ve read through the documentastion but there is nof mentioning of any unit. It does give a example output. This just mentions 1024 MB.
Cache Board Present: True
Cache Status: OK
Cache Ratio: 10% Read / 90% Write
Drive Write Cache: Disabled
Total Cache Size: 2.0
Total Cache Memory Available: 1.8
Battery Backed Cache Size: 1.8
No-Battery Write Cache: Disabled
Cache Backup Power Source: Capacitors
Cache Module Temperature (C): 21