In this blog post, we will explore how to use environment variables in a Node.js script running inside Broadcom VMware VCF Orchestrator. Environment variables are a great way to configure your scripts without hardcoding values, making your code more flexible and secure.
Environment Variables in VCF Orchestrator
For this example, we will use two environment variables available in the VCF Orchestrator environment.
– KAFKAJS_NO_PARTITIONER_WARNING
– NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED
These variables are commonly used when integrating with Kafka or handling TLS certificates in Node.js.
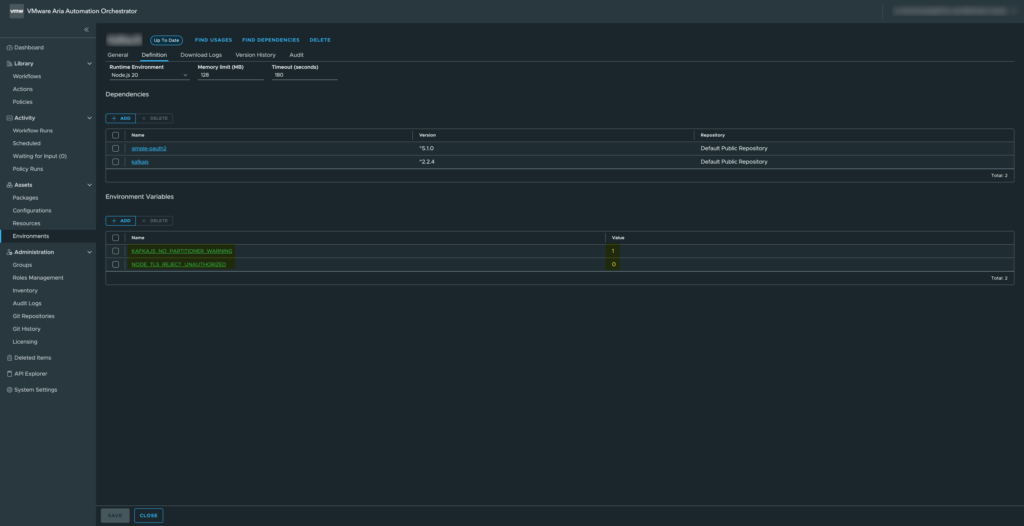
Loading and Validating Environment Variables
Below is a function that retrieves these environment variables and validates their values:
// Load container environment variables
const loadEnvs = () => {
const { KAFKAJS_NO_PARTITIONER_WARNING, NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED } = process.env;
// Validation: only "0" or "1" are allowed
if (!['0', '1'].includes(KAFKAJS_NO_PARTITIONER_WARNING)) {
throw new Error(`${LOG_PREFIX} Invalid KAFKAJS_NO_PARTITIONER_WARNING value: ${KAFKAJS_NO_PARTITIONER_WARNING}`);
}
if (!['0', '1'].includes(NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED)) {
throw new Error(`${LOG_PREFIX} Invalid NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED value: ${NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED}`);
}
// Return the validated variables
return { KAFKAJS_NO_PARTITIONER_WARNING, NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED };
};Explanation: We destructure the variables directly from process.env. Validation ensures the variables are either “0” or “1” only, preventing invalid configurations. The function returns an object with the validated variables, which can be safely used in your script.
Using the Environment Variables
Once loaded, you can use these variables in your Node.js script like this:
// Load environment variables
const envs = loadEnvs();
console.log(`${LOG_PREFIX} Setting environment variable KAFKAJS_NO_PARTITIONER_WARNING=${envs.KAFKAJS_NO_PARTITIONER_WARNING}`);
console.log(`${LOG_PREFIX} Setting environment variable NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED=${envs.NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED}`);This allows you to reference the environment variables throughout your script, for example to configure KafkaJS behavior or TLS certificate validation.
Why This Approach Is Useful
- Centralized configuration: No hardcoding; variables can be changed per environment.
- Fail-fast validation: The script throws an error immediately if a variable has an invalid value.
- Secure defaults: Particularly important for TLS and security-related flags.
- Reproducibility: Works consistently across VCF Orchestrator containers.
This setup ensures that your Node.js scripts in VCF Orchestrator are flexible, secure, and maintainable, while keeping the environment-specific configuration outside your code.